It is an infertility treatment used when a blockage in the fallopian tubes prevents the normal binding of sperm to the egg. Egg cells are removed from a woman's ovaries, and in vitro fertilised. The resulting zygote is placed into the fallopian tube by the use of laparoscopy. The procedure is a spin-off of the gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) procedure.
A technique in which a woman's egg is fertilized outside the body, then implanted in one of her fallopian tubes. This technique is one of the methods used to overcome infertility, the inability of couples to produce offspring on their own.
First, the egg and the male sperm needed to fertilize it are harvested. Then the egg and the sperm are united in a petri dish, a multi-purpose glass or plastic container with a lid. If all goes well, the sperm fertilizes the egg, and the physicians then implant it in a fallopian tube. From there, nature takes its course, and the egg eventually is deposited by the fallopian tube into the uterus (womb) for development.
A zygote is the combined cell resulting from the union of sperm and egg. A zygote develops into an embryo. An embryo, a mass of cells with no recognizable human features, begins formation of a human body. After about seven or eight weeks, the embryo exhibits recognizable features such as a mouth and ears. At this stage, the developing human becomes known as a fetus. The word "zygote" is derived from the Greek word "zygon" (yoke).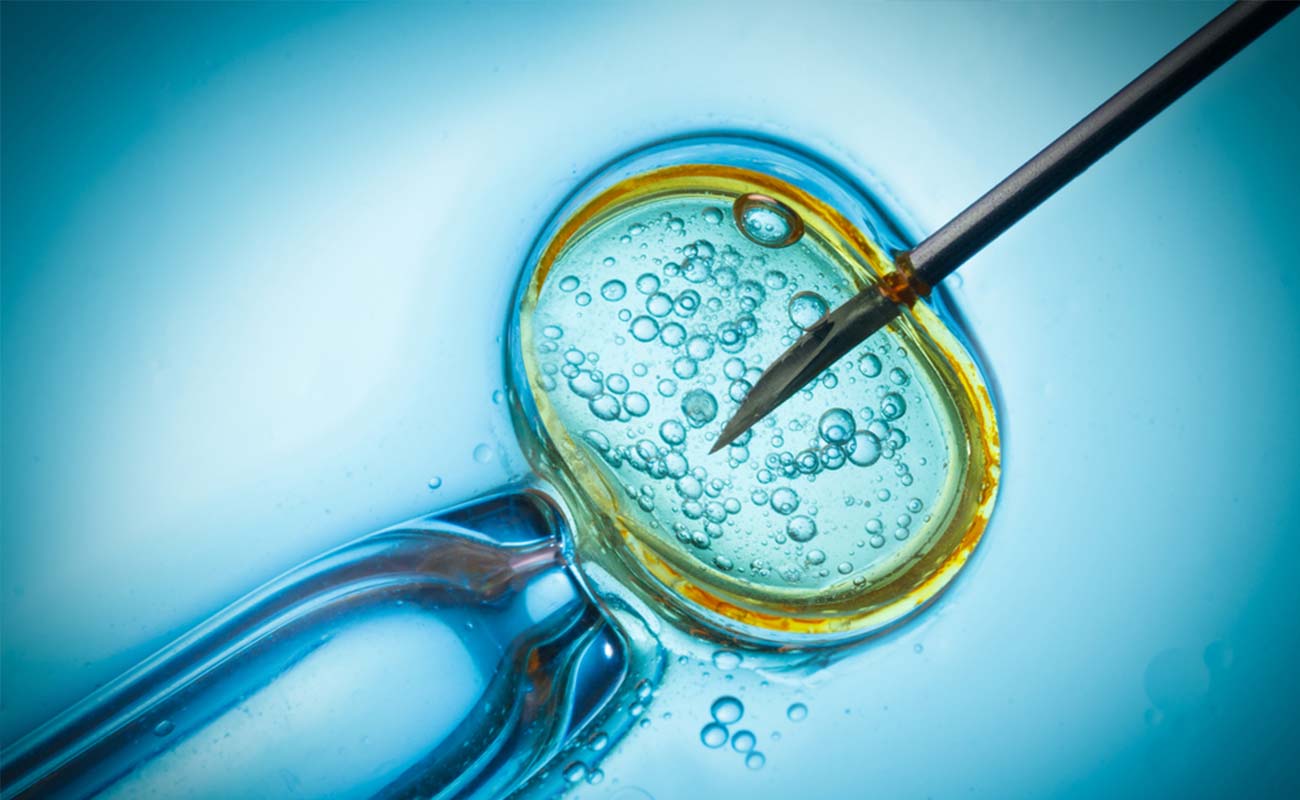
The term "intrafallopian" means "inside the fallopian tubes." ("Intra," a Latin word, means "within" or "inside.") Thus, the term "zygote intrafallopian transfer" refers to the transfer of a zygote into a fallopian tube.
ZIFT is an assisted reproductive procedure that involves the following steps:
ZIFT is an assisted reproductive procedure which may be the selected form of treatment for any infertility problems except the following:

ZIFT is commonly chosen by couples who have failed to conceive after at least one year of trying and who have failed five to six cycles of ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI).
Some couples want to explore more traditional or over the counter efforts before exploring infertility procedures. If you are trying to get pregnant and looking for resources to support your efforts, we invite you to check out the fertility product and resource guide provided by our corporate sponsor.
GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer) and ZIFT (zygote intrafallopian transfer) are modified versions of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Like IVF, these procedures involve retrieving an egg from the woman, combining with sperm in a lab then transferring back to her body, but in GIFT and ZIFT the process goes more quickly. While in traditional IVF the embryos are observed and raised in a laboratory for 3 to 5 days, in ZIFT, the fertilized eggs -- at this stage called zygotes -- are placed in the fallopian tubes within 24 hours. In GIFT, the sperm and eggs are just mixed together before being inserted and, with luck, one of the eggs will become fertilized inside the fallopian tubes.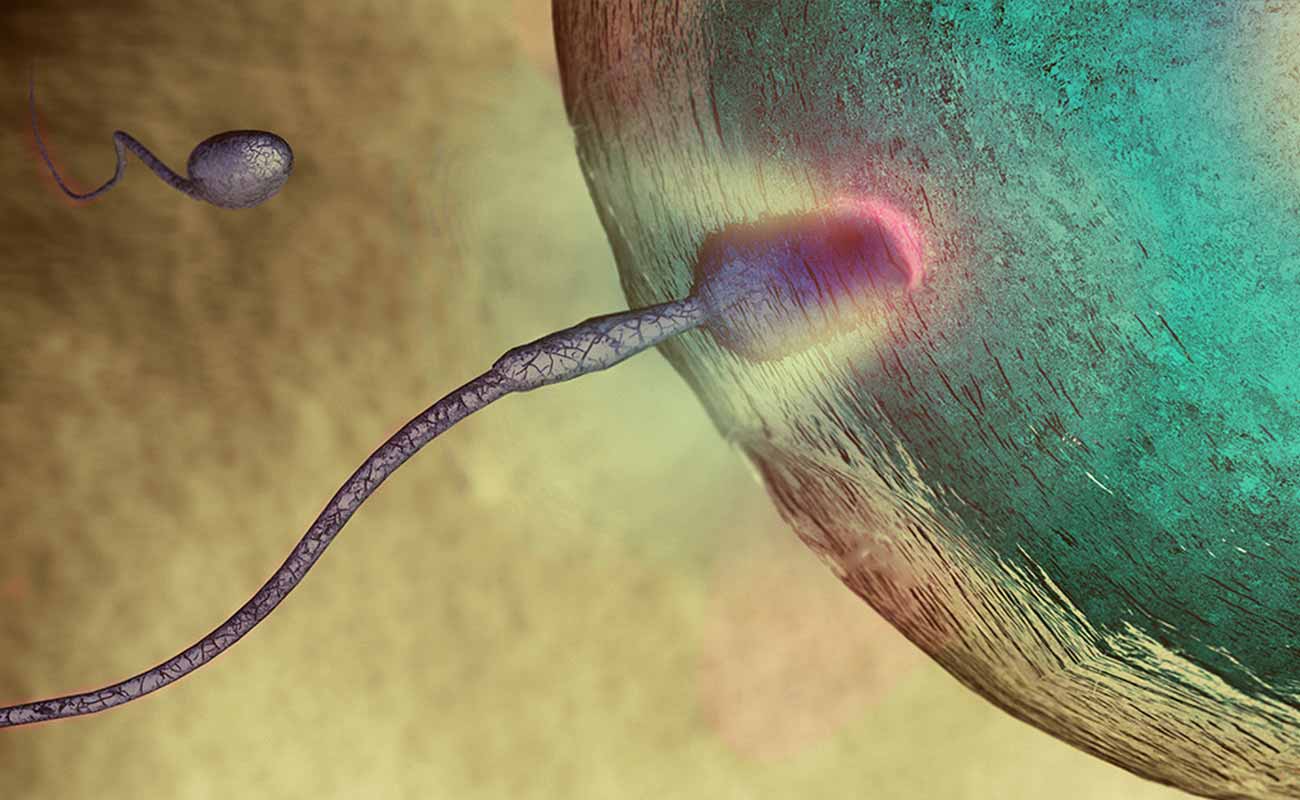
So what's the advantage of these procedures? For some women who haven't been able to get pregnant with normal in vitro fertilization, GIFT or ZIFT may be a good idea. The processes used in GIFT and ZIFT are closer to natural conception. In ZIFT, the eggs are placed in the fallopian tubes rather than directly in the uterus. With GIFT, fertilization actually takes place in the body rather than in a petri dish.
However, in vitro fertilization techniques have become more refined. And since GIFT and ZIFT both require a surgical procedure that IVF does not, IVF is almost always the preferred choice in clinics. In vitro fertilization accounts for at least 98% of all assisted reproductive technology procedures performed in the U.S., while GIFT and ZIFT make up less than 2%.
GIFT and ZIFT can be used to treat many types of infertility, except in cases where there is damage to or abnormalities of the fallopian tubes. These techniques can also be used in cases of mild male infertility, as long as the sperm is capable of fertilizing an egg.
If the woman is not capable of producing eggs that can be used in GIFT, but her partner's sperm is capable of fertilization, they might consider getting eggs from a donor. One reason for using an egg donor is age. Women over age 35 are less likely to have viable eggs and more likely to have children with birth defects than younger women. A woman with premature ovarian failure, a condition in which menopause has begun early, might also consider a donor if she wants to carry a child. Most egg donation is anonymous, but some couples prefer to know their egg donor and take legal steps to contract for the donation of the eggs.
This procedure is similar to GIFT in that the assisted reproduction is done in the fallopian tubes. The difference is that with ZIFT the sperm and egg are mixed together in the laboratory, and given time to fertilize before being placed in the fallopian tubes. In this sense, ZIFT is closer to traditional in vitro fertilization. ZIFT, like GIFT, requires treatment with hormones, and the procedure is performed by laparoscopy. Because ZIFT allows for fertilization to be confirmed. Before the eggs are inserted into the fallopian tubes, fewer eggs are usually used, lowering the risk of multiple pregnancy.
ZIFT has been used in infertility situations where at least one fallopian tube is normal and other treatments have failed; however, the need for two interventions and the fact that IVF results are equal or better (as of 2004), leaves few indications for this procedure. Accordingly, the number of ZIFTs performed has been declining.
Sources: babycenter, webmd, americanpregnancy.org,
Submit Comment