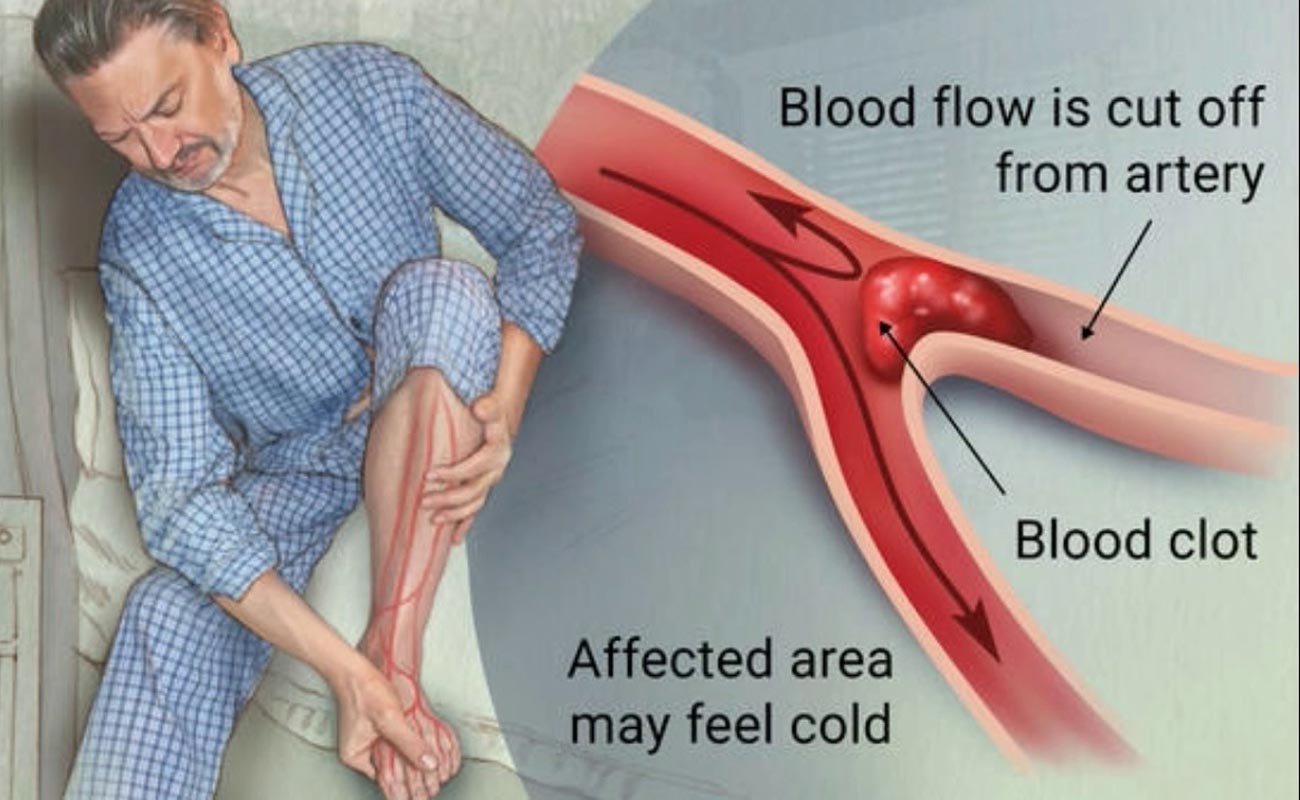
An air embolism, also called gas embolism, happens when one or some gas bubbles enter a vein or artery. It could block the passage of blood. That is why an air embolism is often regarded as a life-threatening disorder.
Considering the place where the blood is blocked, symptoms and severity may vary. It is worth mentioning that air embolism is one of the main causes of mortality among the diving community.
There are so many factors associated with air embolism (the most prevalent of which is diving). Some specific medical procedures may as well create gas bubbles in the blood. The precise incidence rate of air embolisms yet to be known; most of trivial cases can keep going untreated and therefore, the symptoms can be hidden.
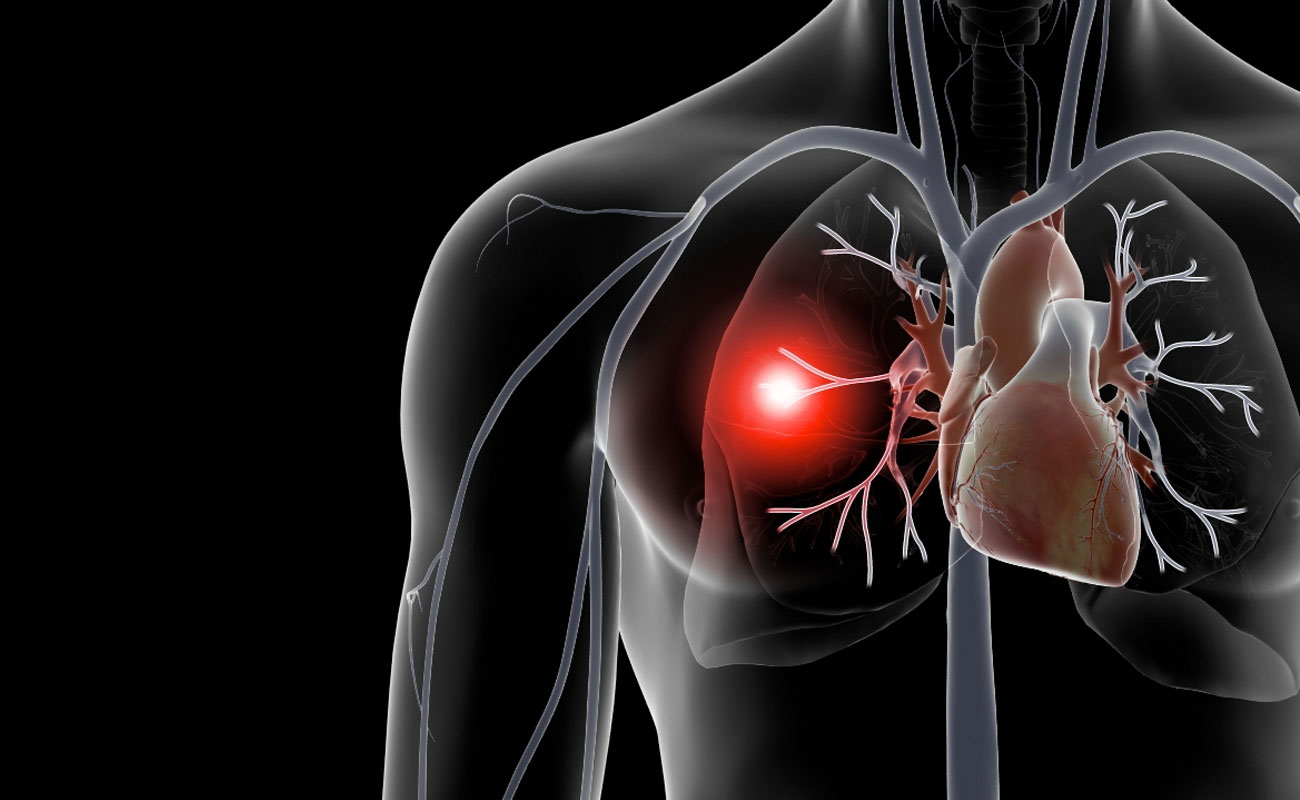
A minor air embolism usually causes very mild or no symptoms at all. However, severe cases of air embolism may be as follows:
• labored breathing or respiratory failure
• pain in chest or heart failure
• feeling pain in muscle or joint
• stroke
• changes in mental status, like confusion or loss of consciousness
• low blood pressure
• blue skin tint
An air embolism may occur if your veins or arteries are cut and exposed, and pressure causes air to go into them. This could occur in many different ways, including:
It is possible that air, accidently, is injected to your veins through a syringe or an IV. It is also possible that air enters your veins or arteries through a catheter.
During surgical procedures air may enter into your veins and arteries. This most commonly happens during brain surgeries. According to an article published in the Journal of Minimal Access Surgery, it is estimated that some 80% of all brain surgeries lead to an air embolism. Nevertheless, surgeons most of the time spot and correct the embolism during the surgery so that it wouldn’t be a severe problem.
Surgeons and nurses know how to prevent air from entering into the veins and arteries during surgical procedures. Also, they are also trained to detect an air embolism and if occurred, treat it immutably.
An air embolism may also happen if there is trauma to your lung. For instance, if your lung is at risk after an accident, a ventilator machine may be used for helping you breathe easier. The ventilator push air into a damaged vein or artery.
Scuba diving
Getting an air embolism in scuba diving is a common occurrence. This might happen when you hold your breath for too long under water or at the time of too fast surfacing from the water.
Doing these things could cause the air sacs in the lungs (known as alveoli) to rupture. If the alveoli rupture happens, air may move to your arteries and consequently an air embolism occures.
An injury that happens as a result of a bomb or blast explosion may open your veins or arteries. These types of injury usually happen in the battlefield or combat situations. Explosion can force air into injured veins or arteries.
As mentioned in the reports of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “blast lung” is the most prevalent fatal injury in those in combat survived blast injuries. Blast lung is referred to lung damages as the result of blast explosion or blast. At this types of embolism, air is pushed into a vein or artery in the lung.
Medical practitioner may suspect that you have gotten an air embolism if you are go through the signs and symptoms. They also study your medical records to know if you have recently had a surgery or lung injury and ask you about the things that might cause an air embolism.
In order to detect air embolisms during surgeries, physicians employ equipment that monitor heart sounds, airway sounds, breathing rate, and blood pressure to spot the condition.
If a medical professionals suspect that that a person has an air embolism, they may carry out a CT scan or ultrasound to make sure or reject the presence of the condition, while identifying its exact location in the body.
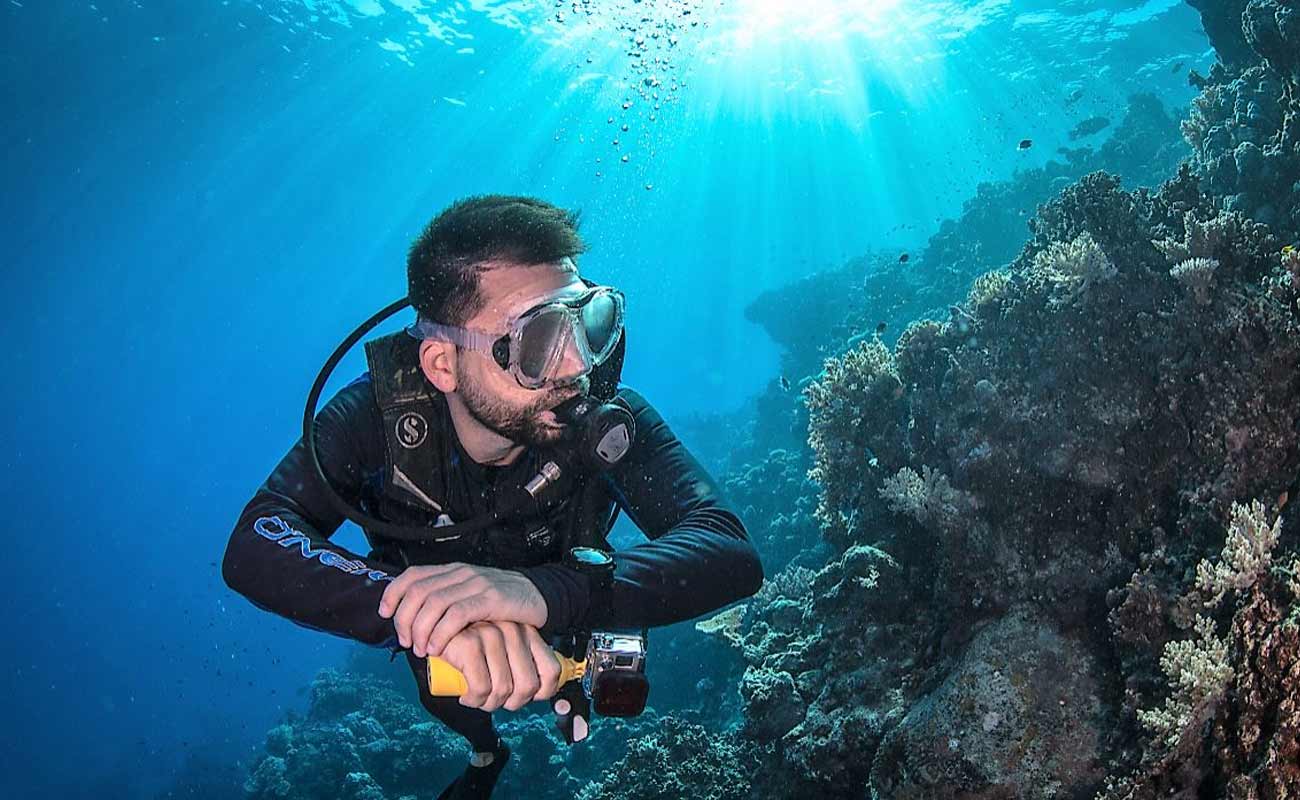

When a diver gets an air embolism, the best and only effective treatment is instant recompression treatment in a certain pressurized room known as “hyperbaric chamber”. Until the diver gets the hyperbaric chamber, he should be given 100 percent oxygen while laid horizontally.
During decompression treatment, the person is laid in hyperbaric chamber, most of the time for many hours. During this time the patient breathes a combination of oxygen and gases under pressure. The high pressure could bring back the normal blood flow and oxygen to the body's tissues as well as reducing the size of the bubbles in the body.
In cases of decompression sickness, the pressure makes the bubbles of nitrogen to be dissolved into the blood cycle.
When the recompression is over, pressure is slowly reduced so that the gases leave the body without deteriorating the difficulty. This procedure is similar to surfacing slowly from a dive. Depending on the severity of symptoms, the treatment may last for several days.
Submit Comment